Software
Managing and Surviving Software Updates
Surviving a firmware, application software or a Windows update can at times seem impossible…

So you put off upgrades and updates as long as possible because you can’t afford the downtime. But doing nothing can put you in a darker place—one where you could be down for much longer than you thought because a hacker got into your old and unprotected system or you can’t find a replacement PLC on eBay for that 30-year old device with an “intermittent CPU or memory.”
Updates may not support older equipment and software
Over the Memorial Day weekend, I built a new Intel-based Core i9 computer to replace my aging 7-year old Core i7. Opting for a new Windows 10 Professional license and Ubuntu Linux 20.04 OS (dual boot), I knew that if I wanted to use an aging film scanner, I’d have to install a Virtual Machine (VM) on Windows 10 or Ubuntu to run Windows XP to support the old device—maybe you’ve faced a similar situation with older industrial equipment. Unfortunately, my 20-year old audio recorder’s software was plain obsolete, but my new TASCAM is compatible with Windows 10.
I now face a “free Windows 11 update” in the future, which I hear occupies 60 gigabytes of disk space. Seriously, do I need all that clutter? At some point, your IT department will be faced with the same upgrade decision—while your OT group struggles to keep its controls operating without downtime. Building and maintaining hardware is one thing, but dealing with Windows forced updates and migrating application software can be a painstaking process—and full of pitfalls—but when successful, with rewards.
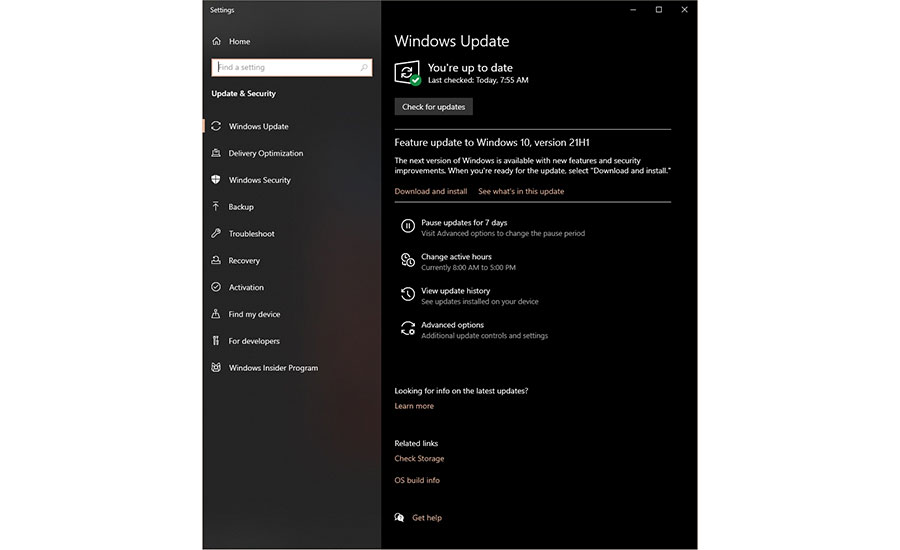 Scheduling Windows Updates is not necessarily so easy as you can only put them off for so long. Admins have more control by making changes in the Windows Group Policy Editor or the system registry. Image courtesy of: Screen dump, Wayne Labs (Click on image to enlarge.)
Scheduling Windows Updates is not necessarily so easy as you can only put them off for so long. Admins have more control by making changes in the Windows Group Policy Editor or the system registry. Image courtesy of: Screen dump, Wayne Labs (Click on image to enlarge.)
One way around the Windows forced-updates issue is to choose industrial applications that also are available on Linux, for example, Inductive Automation’s Ignition. Though most Linux distributions are available out of the box with automatic updates turned on (for example, I use Ubuntu 18.04 Server and 18.04/20.04 workstations), they’re so configurable that the user controls the OS—not the other way around.
I asked automation hardware suppliers, process control software folks and system integrators for some advice on dealing with Windows, control application software and device firmware updates.
Dealing—or not dealing—with Windows updates
In dealing with Windows updates, the experts I interviewed had varying opinions, but one thing they agreed on is to approach upgrading Windows-based workstations on the plant floor with caution.
Staying on top of Windows system updates is critical to security and performance, but many organizations have to be careful about update timing to avoid production interruptions, says Sesh Natarajan, Emerson DeltaV product director. Organizations need the flexibility to be able to decide when and what to update to minimize the impact to operations.
“With system updates, the best offense is a good defense. If automation leaders are strategic about how they handle operating system updates and perform due diligence to test a wide variety of installations, they can mitigate many of the risks of an update breaking an application or disrupting production,” says Natarajan.
ADISRA is a Windows-based HMI/SCADA package especially designed for machine builders and OEMs. According to Bruno Armond Crepaldi, chief technology officer at ADISRA, major Windows updates should be kept off production systems until the updates are tested for stability and compatibility issues. “Many times, we recommend that customers stay one [Windows] release behind so their production system remains stable, and early issues with a new released update can be identified and resolved before being placed on production systems. This advice is given with the assumption that the update is not a major security release and that the production machines are adequately secured from outside intrusions.” Crepaldi advises turning off auto-updates for production machines, or at least delaying them as long as possible.
Chris Schulze, VP sales at CODESYS Corporation, a Control System Integrators Association (CSIA) member, is adamant about shutting down Windows semi-annual updates. “No semi-annual or annual changes.” Only if major hardware (major machine system) gets changed or updated. It should be an IT and OT responsibility. The update decision should come from the OT alone. Schulze thinks Windows shouldn’t even be a plant floor consideration: “Please note, the number one OS for PC-based automation is Linux, and not Windows anymore.”
Some automation suppliers have gone the non-Windows route for their devices and controllers. “In many of its data acquisition units, controllers, PLCs and other products, Yokogawa has opted NOT to use the Windows operating systems due to the frequent upgrades and security patches required over time,” says Gerald Hardesty, product marketing manager, Yokogawa Corporation of America, Industrial Automation Products. Instead, Yokogawa has opted to use an alternative real-time embedded operating system to avoid these security issues and threats. Yokogawa products are less susceptible to the vulnerabilities that Windows systems are exposed to, and thus the routine security upgrades that Windows users undergo are required far less often, or not at all.
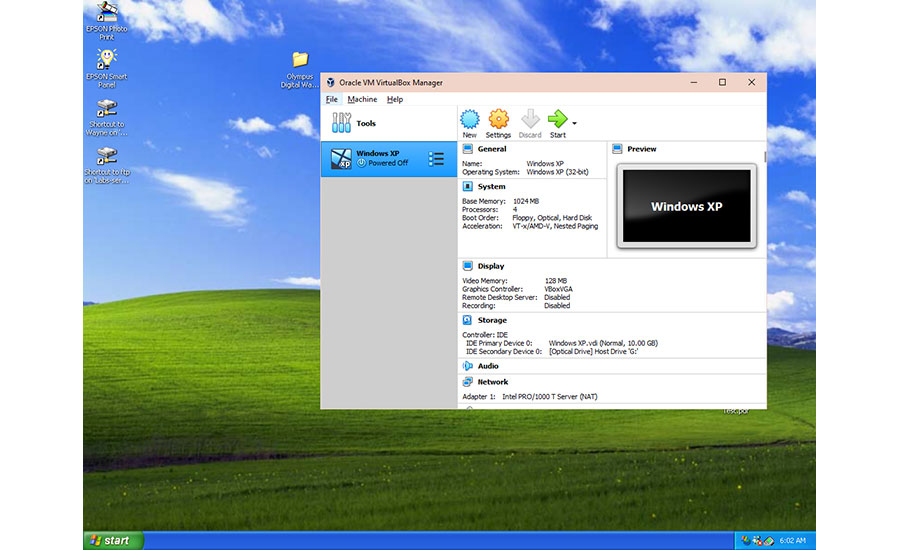 Oracle’s VM VirtualBox is available for non-commercial and commercial applications and allows the running of one operating system (shown here, Windows XP) inside another OS—in this case Windows 10. The virtual machine (VM) allows Windows XP to run older applications—such as an old film scanner or an I/O system—while enjoying the protection of the host operating system, Windows 10. VirtualBox is available for Mac OS, Windows, Linux and Oracle Solaris. Image courtesy of: Screen dump, Wayne Labs (Click on image to enlarge.)
Oracle’s VM VirtualBox is available for non-commercial and commercial applications and allows the running of one operating system (shown here, Windows XP) inside another OS—in this case Windows 10. The virtual machine (VM) allows Windows XP to run older applications—such as an old film scanner or an I/O system—while enjoying the protection of the host operating system, Windows 10. VirtualBox is available for Mac OS, Windows, Linux and Oracle Solaris. Image courtesy of: Screen dump, Wayne Labs (Click on image to enlarge.)
Scheduling application and Windows updates
Interestingly enough, application providers with cloud-based systems can make their own upgrades easier on users because often all that is required to use them is a web browser. Nevertheless, IFS is very sensitive to updates in regulated industries. IFS provides integrated HACCP and quality control, advanced demand planning and forecasting, supply chain management systems and much more. “IFS Cloud marks the start of a new, twice-yearly feature update cadence for an ‘evergreen’ customer experience,” says Antony Bourne, IFS senior vice president - industries.
“Historically we have made large core releases every two to three years, with quarterly updates containing a combination of fixes and new features,” says Bourne. “With IFS Cloud we now have twice-yearly releases of new functionality, each supported through monthly service updates that only contain fixes.”
In many cases, processors operating under particularly rigid regulatory requirements (e.g. FDA), have requested flexibility regarding the timing of update adoption in their production environment. IFS has chosen to offer the flexibility required for these customers, (via a defined time window where IFS provides access to the update), to determine when the time is right for them to push a new version to their environments. Having this flexibility is essential where any change to IT systems is likely to trigger the requirement for a new third-party audit before rolling it out into production.
 ADISRA SmartView provides modern visualization and deployment options for HMI/SCADA functionality. Image courtesy of: ADISRA (Click on image to enlarge.)
ADISRA SmartView provides modern visualization and deployment options for HMI/SCADA functionality. Image courtesy of: ADISRA (Click on image to enlarge.)
Back at the machine/plant level, Allpax, maker of retorts and other production equipment, is careful with Windows updates. “Updates to the PCs (both servers and clients) in our system are scheduled during production downtime windows,” says Jonathan Watkins, VP of technology. Tests are performed to ensure that the updates do not adversely affect the system before production is resumed. These updates are coordinated with the local group that manages IT system for the customer.
Automated Systems Group, a CSIA member, stresses the importance of keeping automation up and running. “In our experience at AMT, any time you update Windows, there is a chance that other installed programs may not continue to work,” says Terry Meister, controls engineering manager. Some may encounter “bugs” when the Windows software is updated. “Also, we have found that the manufacturers of industrial hardware equipment lag behind the Windows updates, making sure their software will work well with the updates before releasing their own updates. For this reason, it is important that the admin and PLC programmers/maintenance discuss when the appropriate time is to update. Also, making sure that enough downtime is scheduled with production—in case issues arise—can save all a lot of heartache,” says Meister.
Typical system vendors for industrial applications will evaluate updates and roll out changes as appropriate, says Steve Pflantz, P.E./P. Eng., CRB associate. “Make sure you understand if it is ever advised to do any updates to an industrial system without them reviewing the update.” Industrial applications are a more substantial application than most, and updates of any kind to the operating system need to be verified to not cause a problem. This is the fundamental reason to manage a system according to the vendor’s guidelines.
While Travis Cox, co-director of sales engineering at Inductive Automation says that major updates should not be put on hold, it’s extremely important to stay up to date and avoid OS obsolescence. The problem is, however, that most OT applications rely on specific OS versions and likely won’t run on the newest version. Often the upgrade path is difficult and expensive, leading manufacturers to put the major updates on hold and putting themselves at risk. Software vendors need to take this into consideration and provide simple upgrade paths.
IT and OT must work as a team
Communication between IT and OT professionals is key, especially when it comes to updates, says Keith Mandachit, P.E., engineering manager at Huffman Engineering, a Certified CSIA member. From an OT perspective, all updates should really be delayed until there has been an opportunity to check with the manufacturer and have it cleared to be installed. In an ideal world, organizations would have a separate test environment that wouldn’t potentially disrupt the entire production line. This is one reason it is vital to bring in a control system integrator at the beginning of the project so these discussions can be held prior to design, updates or upgrades.
 More savings in maintenance and servicing of the device software are made possible via the cloud by the ctrlX Device Portal powered by NEXEED. Image courtesy of: Bosch-Rexroth (Click on image to enlarge.)
More savings in maintenance and servicing of the device software are made possible via the cloud by the ctrlX Device Portal powered by NEXEED. Image courtesy of: Bosch-Rexroth (Click on image to enlarge.)
OT and IT should work together on a patching strategy, says Cox. OT can help determine when to perform the updates or deploy strategies to allow updates without disrupting operations, such as redundancy. IT can provide OT sandbox environments to test out the latest update to understand whether they will be affected. Developing a procedure and strategy is critical and allows the organization to stay ahead of the updates. It also buys time to work with software vendors when issues have been identified. “You don’t want to find out about issues after it’s too late, and be forced to stay on older versions because of incompatibilities,” he adds.
This seems like a great opportunity to introduce collaboration between OT and IT teams as a Windows HMI is usually a shared asset among the key stakeholders, says Luis Narvaez, Siemens product marketing manager, basic automation & industrial security. “While it is important to ensure that your Microsoft/Windows products are always up-to-date with all of the latest security/functional patches, it is also equally important to verify with the vendor of whatever industrial applications whether those updates will be compatible with their software in order to avoid potential downtime and thus security vulnerabilities.” Siemens has a web page where users can verify compatibility of their software products with tested Microsoft or other third-party products via www.siemens.com/kompatool.
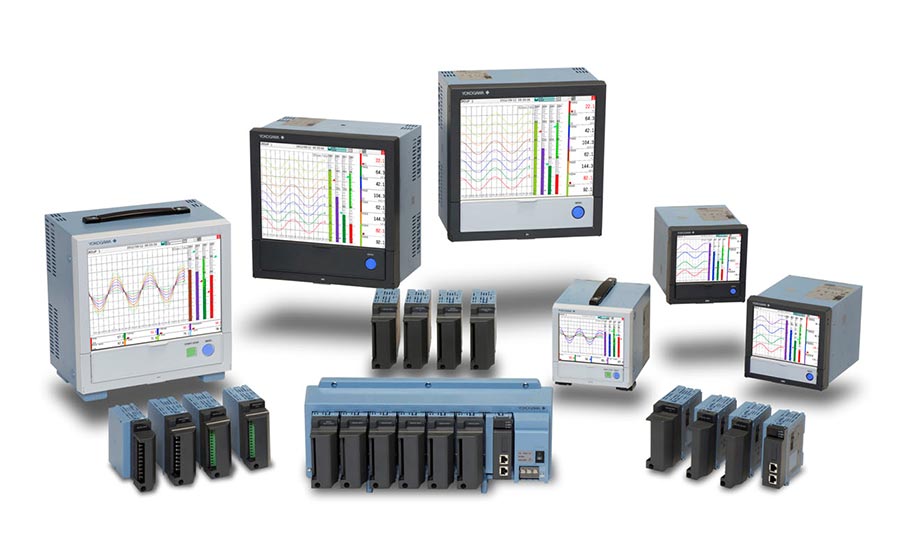 A variety of devices, each not dependent on frequent software updates, are available from Yokogawa for securely storing data. Source: Yokogawa (Click on image to enlarge.)
A variety of devices, each not dependent on frequent software updates, are available from Yokogawa for securely storing data. Source: Yokogawa (Click on image to enlarge.)
Let system integrators handle updates
We’ve already seen that application developers work behind the scenes to keep their software up to date so Windows updates don’t break a control system. “We develop and test all of our systems with current OS and software with current updates (patches),” says Jerry Leuthold, senior project manager, Bachelor Controls Inc, a CSIA Certified Member. “Then we install the system at the customer site and recommend that it is secured and has no access to the internet. Only tested OS and software patches would then be applied to the system manually.”
For those processors who have broken their system by downloading a Windows update, Leuthold says VMs and good backups can get a manufacturer back in operation to a state before a system was broken.
“This is a hard lesson,” says Meister. “If an end user is looking to update software on a machine connected to a PC or PLC, they should contact the integrator before proceeding. Before they shut down for the update, we can investigate and ensure what is needed to get them back up and running.”
Meister also suggests a good reason for using a VM. “We will use VMWare with older versions of Windows as necessary. This allows us to keep our main computer system up to date for security reasons and have a VM for PLC programs as needed.”
OS and application updates can break systems as Huffman’s Sean Creager, senior electrical engineer, describes one situation where an update crashed an application. “At the time we just had to roll back and uninstall the update until a Hot Fix was provided by the manufacturer. In very specific situations we have actually set up the system to turn off Windows updates because of the potential consequences of interference.”
Control system updates
In this article we’ve looked at dealing with Windows system updates. In another article, “System integrators and hardware suppliers look at the mechanics of controls updates,” I ask system integrators and automation suppliers how they work with users to deliver automation updates safely and efficiently. We also look at the importance of backups in updating automation software and equipment.
For more information:
- ADISRA, www.adisra.com
- Allpax, www.allpax.com
- Automated Systems Group, www.appliedmfg.com
- Bachelor Controls, Inc, www.bachelorcontrols.com
- Bosch Rexroth – Electric Drives and Controls, www.boschrexroth-us.com
- CODESYS, www.codesys.us
- CRB, www.crb.com
- Emerson, www.emerson.com
- Endress+Hauser USA, us.endress.com
- Huffman Engineering, www.huffmaneng.com
- IFS, www.ifs.com
- Inductive Automation, inductiveautomation.com
- Interstates, www.interstates.com
- Malisko Engineering, malisko.com
- Rockwell Automation, www.rockwellautomation.com
- Siemens, www.usa.siemens.com/somatic
- Yokogawa Corporation of America, Yokogawa.com/us
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!









